Amazon class sloop
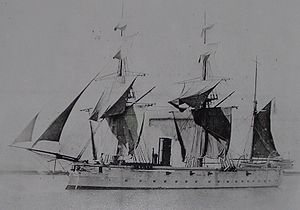 HMS Dryad at anchor, with sails airing | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Amazon-class sloops |
| Builders: | Pembroke Dockyard Devonport Dockyard |
| Operators: | |
| Built: | 1865–1866 |
| In commission: | 1865–1885 |
| Completed: | 6 |
| Lost: | 2 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Screw sloop |
| Displacement: | 1574 tons |
| Length: | 187 ft (57 m) |
| Beam: | 36 ft (11 m) |
| Draught: | 17 ft (5.2 m)[1] |
| Installed power: | 300 horsepower[1] |
| Propulsion: |
Two-cylinder horizontal single-expansion steam engine Single screw |
| Complement: | 150[1] |
| Armament: |
As built:
|
The Amazon class was a class of six screw-sloops of wooden construction built for the Royal Navy between 1865 and 1866.
Construction
Design
Designed by Edward Reed[2], the Royal Navy Director of Naval Construction, they were equipped with a ram bow.[2] The hull was of wooden construction, but they were the first class of sloops to incorporate a form of composite construction; they had iron cross beams while retaining wooden framing.[2]
Propulsion
Propulsion was provided by a two-cylinder horizontal single-expansion steam engine by Ravenhill, Salkeld & Company driving a single 15 ft (4.6 m) screw. Vestal and Nymphe were fitted with three-cylinder Maudslay engines.[2]
Sail plan
All the ships of the class were built with a barque rig.[2]
Armament
The class was designed with two 7-inch (6½-ton) muzzle loading rifled guns mounted on slides on centre-line pivots, and two 64-pounder muzzle loading rifled guns on broadside trucks. Dryad, Nymphe and Vestal were rearmed in the early 1870s with an armament of nine 64-pounder muzzle loading rifled guns, four each side and a centre-line pivot mount at the bow.[2]
Ships
| Name | Ship Builder | Launched | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMS Amazon | Pembroke Dockyard | 1865 | Sunk in collision with SS Osprey, off Start Point, English Channel 10 July 1866[1] |
| HMS Vestal | Pembroke Dockyard | 1865 | Sold to Castle for breaking in December 1884[2] |
| HMS Niobe | Devonport Dockyard | 1866 | Wrecked off Cape Blanc on Miquelon Island, off the Atlantic Coast of Newfoundland and Labrador 21 May 1874[1] |
| HMS Dryad | Devonport Dockyard | 1866 | Sold in September 1885 and broken up in April 1886[2] |
| HMS Daphne | Pembroke Dockyard | 1866 | Sold for breaking on 7 November 1882[2] |
| HMS Nymphe | Devonport Dockyard | 1866 | Sold for breaking in December 1884[2] |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Cruisers at Battleships-Cruisers website". http://www.battleships-cruisers.co.uk/cruisers.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Winfield, Rif; Lyon, David (2003). The Sail and Steam Navy List, 1815-1889. Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1861760326.
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: the complete record of all fighting ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham. ISBN 9781861762818. OCLC 67375475.
| ||||||||
